Markets
Market Complexity Could Trigger the Next Crash
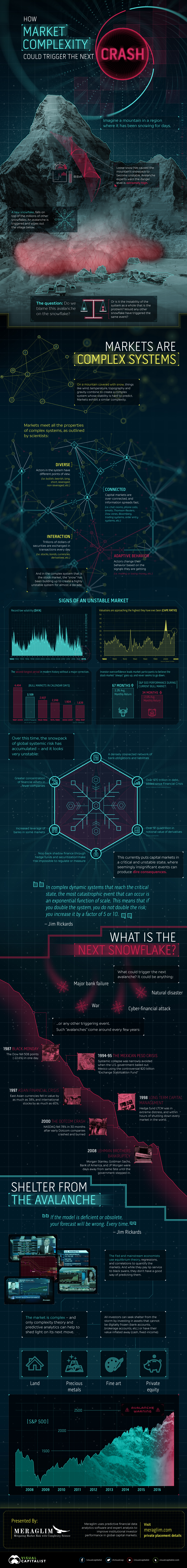
How Market Complexity Could Trigger the Next Crash
Complex systems are all around us.
By one definition, a complex system is any system that features a large number of interacting components (agents, processes, etc.) whose aggregate activity is nonlinear (not derivable from the summations of the activity of individual components) and typically exhibits hierarchical self-organization under selective pressures.
In today’s infographic from Meraglim we use accumulating snow and an impending avalanche as an example of a complex system – but really, such systems can be found everywhere. Weather is another complex system, and ebb and flow of populations is another example.
Markets are Complex Systems
Just like in the avalanche example, where various factors at the top of a mountain (accumulating volumes of snow, weather, temperature, geology, gravity, etc.) make up a complex system that is difficult to predict, markets are similarly complex.
In fact, markets meet all the properties of complex systems, as outlined by scientists:
1. Diverse
System actors have different points of view. (i.e. bullish, bearish, long, short, leveraged, non-leveraged, etc.)
2. Connected
Capital markets are over-connected, and information spreads fast. (i.e. chat rooms, phone calls, emails, Thomson Reuters, Dow Jones, Bloomberg, trading systems, order entry systems, etc.)
3. Interaction
Trillions of dollars of securities are exchanged in transactions every day (i.e. stocks, bonds, currencies, derivatives, etc.)
4. Adaptive Behavior
Actors change their behavior based on the signals they are getting (i.e. making or losing money, etc.)
And like the avalanche example, where a single snowflake can trigger a much bigger event, there are increasing signs that the complexity behind the stock market has also reached a critical state.
Markets in a Critical State
Here are just some examples that show how the market has entered into an increasingly critical state:
Record-Low Volatility
The VIX, an index that aims to measure the volatility of the market, hit all-time lows this summer.
Bull Market Length
Meanwhile, the current bull market (2009-present) is the second-longest bull market in modern history at 3,109 days. The only bull market that was longer went from the 1987 crash to the Dot-com bust.
Valuations at Highs
Stock valuations, based on Robert Schiller’s CAPE ratio (which looks at cyclically-adjusted price-to-earnings), are approaching all-time highs as well. Right now, it sits 83.3% higher than the historical mean of 16.8. It was only higher in 1929 and 2000, right before big crashes occurred.
Market Goes Up
Investor overconfidence leads investors to believe the market only goes up, and never goes down. Indeed, in this bull market, markets have gone up 67 of the months (an average gain of 3.3%), and have gone down only 34 months (average drop of -2.6%).
Here are some additional signs of systemic risk that make complex markets less stable:
- A densely connected network of bank obligations and liabilities
- Over $70 trillion in debt added since Financial Crisis
- Over $1 quadrillion in notional value of derivatives
- Non-bank shadow finance through hedge funds and securitization make risk impossible to measure
- Increased leverage of banks in some markets
- Greater concentration of financial assets in fewer companies
In other words, there are legitimate reasons to be concerned about “snow” accumulation – and any such “snowflake” could trigger the avalanche.
In complex dynamic systems that reach the critical state, the most catastrophic event that can occur is an exponential function of scale. This means that if you double the system, you do not double the risk; you increase it by a factor of five or 10
– Jim Rickards, author of Road to Ruin
The Next Snowflake
What could trigger the next avalanche? It could be anything, including the failure of a major bank, a natural disaster, war, a cyber-financial attack, or any other significant event.
Such “snowflakes” come around every few years:
1987: Black Monday
The Dow fell 508 points (-22.6%) in one day.
1994-95: The Mexican peso crisis
Systemic collapse narrowly avoided when the U.S. government bailed out Mexico using the controversial $20 billion “Exchange Stabilization Fund”.
1997: Asian financial crisis
East Asian currencies fell in value by as much as -38%, and international stocks by as much as -60%.
1998: Long Term Capital Management
Hedge fund LTCM was in extreme distress, and within hours of shutting down every market in the world.
2000: The Dotcom crash
Nasdaq fell -78% in 30 months after early Dotcom companies crashed and burned.
2008: Lehman Brothers bankruptcy
Morgan Stanley, Goldman Sachs, Bank of America, and J.P. Morgan were days away from same fate until government stepped in.
Shelter from the Avalanche
The Fed and mainstream economists use equilibrium theory, regressions, and correlations to quantify the markets. And while they pay lip-service to black swans, they don’t have a good way of forecasting them or predicting them.
Markets are complex – and only complexity theory and predictive analytics can help to shed light on their next move.
Alternatively, investors can seek shelter from the storm by investing in assets that cannot be digitally frozen (bank accounts, brokerage accounts, etc.) or have their value inflated away (cash, fixed-income). Such assets include land, precious metals, fine art, and private equity.
Markets
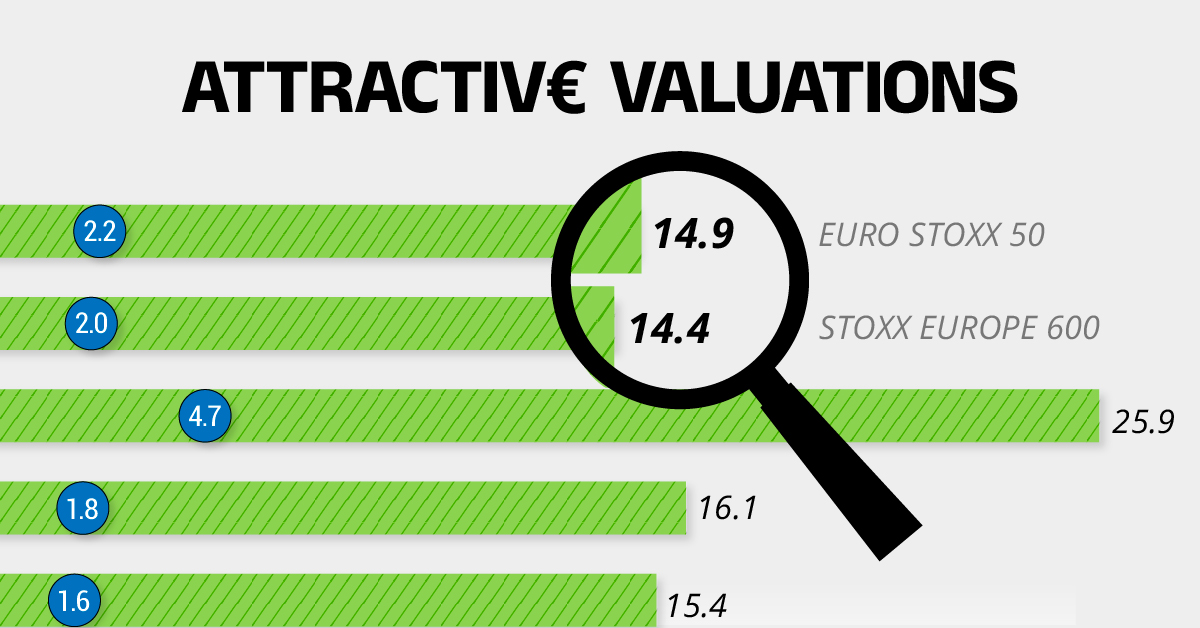
The European Stock Market: Attractive Valuations Offer Opportunities
On average, the European stock market has valuations that are nearly 50% lower than U.S. valuations. But how can you access the market?
European Stock Market: Attractive Valuations Offer Opportunities
Europe is known for some established brands, from L’Oréal to Louis Vuitton. However, the European stock market offers additional opportunities that may be lesser known.
The above infographic, sponsored by STOXX, outlines why investors may want to consider European stocks.
Attractive Valuations
Compared to most North American and Asian markets, European stocks offer lower or comparable valuations.
| Index | Price-to-Earnings Ratio | Price-to-Book Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| EURO STOXX 50 | 14.9 | 2.2 |
| STOXX Europe 600 | 14.4 | 2 |
| U.S. | 25.9 | 4.7 |
| Canada | 16.1 | 1.8 |
| Japan | 15.4 | 1.6 |
| Asia Pacific ex. China | 17.1 | 1.8 |
Data as of February 29, 2024. See graphic for full index names. Ratios based on trailing 12 month financials. The price to earnings ratio excludes companies with negative earnings.
On average, European valuations are nearly 50% lower than U.S. valuations, potentially offering an affordable entry point for investors.
Research also shows that lower price ratios have historically led to higher long-term returns.
Market Movements Not Closely Connected
Over the last decade, the European stock market had low-to-moderate correlation with North American and Asian equities.
The below chart shows correlations from February 2014 to February 2024. A value closer to zero indicates low correlation, while a value of one would indicate that two regions are moving in perfect unison.
| EURO STOXX 50 | STOXX EUROPE 600 | U.S. | Canada | Japan | Asia Pacific ex. China |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EURO STOXX 50 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.24 | 0.43 |
| STOXX EUROPE 600 | 1.00 | 0.56 | 0.71 | 0.28 | 0.48 | |
| U.S. | 1.00 | 0.73 | 0.12 | 0.25 | ||
| Canada | 1.00 | 0.22 | 0.40 | |||
| Japan | 1.00 | 0.88 | ||||
| Asia Pacific ex. China | 1.00 |
Data is based on daily USD returns.
European equities had relatively independent market movements from North American and Asian markets. One contributing factor could be the differing sector weights in each market. For instance, technology makes up a quarter of the U.S. market, but health care and industrials dominate the broader European market.
Ultimately, European equities can enhance portfolio diversification and have the potential to mitigate risk for investors.
Tracking the Market
For investors interested in European equities, STOXX offers a variety of flagship indices:
| Index | Description | Market Cap |
|---|---|---|
| STOXX Europe 600 | Pan-regional, broad market | €10.5T |
| STOXX Developed Europe | Pan-regional, broad-market | €9.9T |
| STOXX Europe 600 ESG-X | Pan-regional, broad market, sustainability focus | €9.7T |
| STOXX Europe 50 | Pan-regional, blue-chip | €5.1T |
| EURO STOXX 50 | Eurozone, blue-chip | €3.5T |
Data is as of February 29, 2024. Market cap is free float, which represents the shares that are readily available for public trading on stock exchanges.
The EURO STOXX 50 tracks the Eurozone’s biggest and most traded companies. It also underlies one of the world’s largest ranges of ETFs and mutual funds. As of November 2023, there were €27.3 billion in ETFs and €23.5B in mutual fund assets under management tracking the index.
“For the past 25 years, the EURO STOXX 50 has served as an accurate, reliable and tradable representation of the Eurozone equity market.”
— Axel Lomholt, General Manager at STOXX
Partnering with STOXX to Track the European Stock Market
Are you interested in European equities? STOXX can be a valuable partner:
- Comprehensive, liquid and investable ecosystem
- European heritage, global reach
- Highly sophisticated customization capabilities
- Open architecture approach to using data
- Close partnerships with clients
- Part of ISS STOXX and Deutsche Börse Group
With a full suite of indices, STOXX can help you benchmark against the European stock market.

Learn how STOXX’s European indices offer liquid and effective market access.

-

 Economy2 days ago
Economy2 days agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
U.S. debt interest payments have surged past the $1 trillion dollar mark, amid high interest rates and an ever-expanding debt burden.
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
We visualized the top U.S. companies by employees, revealing the massive scale of retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
This graphic shows the states with the highest real GDP growth rate in 2023, largely propelled by the oil and gas boom.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
In this graphic, we show the highest earning flight routes globally as air travel continued to rebound in 2023.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
The U.S. residential real estate market is worth a staggering $47.5 trillion. Here are the most valuable housing markets in the country.
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries